How to Read Excel File Matlab Every 5th Row
Writer: Oscar Cronquist Commodity last updated on September 11, 2021
I will in this commodity demonstrate several techniques that extract or filter records based on ii conditions applied to a single column in your dataset. For example, if you utilise the array formula then the result will refresh instantly when you enter new first and end values.
The remaining built-in techniques need a niggling more transmission work in order to apply new conditions, however, they are fast. The downside with the array formula is that information technology may become slow if y'all are working with huge amounts of data.
I have as well written an article in case yous need to find records that match one status in one column and another condition in some other column. The following article shows y'all how to build a formula that uses an arbitrary number of conditions: Extract records where all criteria match if not empty
This article Extract records between 2 dates is very similar to the current one you are reading right now, Excel dates are actually numbers formatted as dates in Excel. If yous desire to search for a text string within a given date range and so read this commodity: Filter records based on a engagement range and a text cord
I must recommend this article if y'all want to practise a wildcard search beyond all columns in a data set, it also returns all matching records. If you lot desire to extract records based on criteria and not a numerical range and so read this part of this commodity.
What is on this page?
- Excerpt all rows from a range based on range criteria (Array formula)
- Video
- How to enter an assortment formula
- Explaining assortment formula
- Extract all rows from a range based on range criteria - Excel 365
- Explaining formula
- Extract all rows from a range based on multiple conditions (Array formula)
- Explaining array formula
- Extract all rows from a range based on multiple atmospheric condition - Excel 365
- Explaining formula
- Extract all rows from a range based on range critera
[Excel defined Tabular array] - Excerpt all rows from a range based on range critera
[Filter] - Excerpt all rows from a range based on range criteria
[Advanced Filter] - Go Excel file
1. Extract all rows from a range based on range criteria
[Assortment formula]
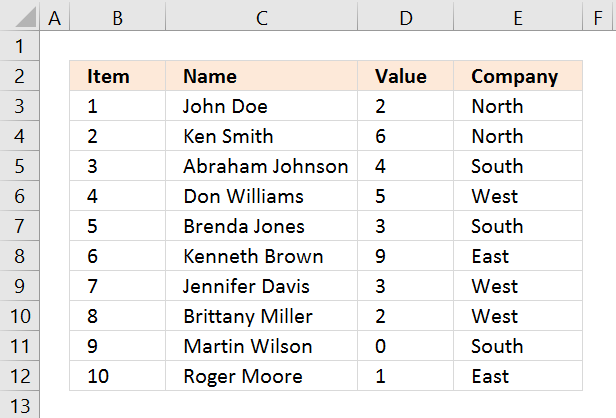
The motion picture above shows you a dataset in prison cell range B3:E12, the search parameters are in D14:D16. The search results are in B20:E22.
Update twenty Sep 2017, a smaller formula in jail cell A20.
Array formula in cell A20:
=Alphabetize($B$3:$East$12, SMALL(IF((INDEX($B$iii:$Eastward$12, , $D$16)< =$D$15)*(Index($B$3:$E$12, , $D$16)> =$D$14), Match(ROW($B$3:$E$12), ROW($B$iii:$East$12)), ""), ROWS(B20:$B$twenty)), COLUMNS($A$i:A1))
Back to top
1.ane Video
See this video to learn more than about the formula:
Back to top
one.2 How to enter this array formula
- Select cell A20
- Paste above formula to prison cell or formula bar
- Press and hold CTRL + SHIFT simultaneously
- Press Enter once
- Release all keys
The formula bar now shows the formula with a beginning and ending curly bracket, that is if you did the to a higher place steps correctly. Similar this:
{=array_formula}
Don't enter these characters yourself, they announced automatically.
Now re-create cell A20 and paste to cell range A20:E22.
Back to top
one.three Explaining array formula in cell A20
You can follow along if you select jail cell A19, become to tab "Formulas" on the ribbon and press with left mouse button on the "Evaluate Formula" push button.
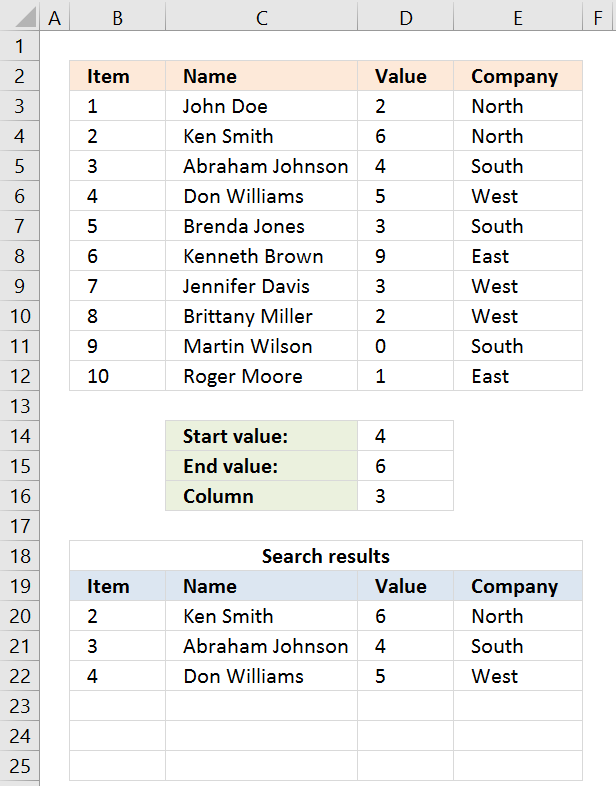
Stride i - Filter a specific column in cell range B3:E12
The Index role is by and large used for getting a unmarried value from a given prison cell range, however, it can as well return an entire column or row from a cell range.
This is exactly what I am doing here, the column number specified in cell D16 determines which column to extract.
Index($B$3:$E$12, , $D$16, 1)
becomes
Alphabetize($B$iii:$E$12, , 3, 1)
and returns C3:C12.
How to use the INDEX function
Step 2 - Check which values are smaller or equal to status
The smaller than and equal sign are logical operators that allow y'all compare value to value, in this case, if a number is smaller than or equal to some other number.
The output is a boolean value, Truthful och Faux. Their positions in the array stand for to the positions in the cell range.
Alphabetize($B$three:$E$12, , $D$16, 1)< =$D$15
becomes
C3:C12< =$D$15
becomes
{2; 6; 4; 5; 3; 9; three; 2; 0; i}<=6
and returns
{TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; Truthful; Truthful; Faux; TRUE; TRUE; True; TRUE}.
Step 3 - Multiply arrays - AND logic
In that location is a second condition nosotros need to evaluate before we know which records are in range.
(Alphabetize($B$3:$E$12, , $D$16, 1)< =$D$15)*(Index($B$3:$E$12, , $D$xvi, ane)> =$D$xiv)
becomes
({2; 6; 4; 5; 3; ix; 3; two; 0; ane}< =$C$xiv)*({two; 6; 4; five; 3; nine; 3; ii; 0; 1}> =$C$13)
becomes
({two; 6; 4; v; iii; 9; 3; 2; 0; one}< =iii)*({2; six; 4; 5; 3; 9; iii; 2; 0; i}> =0)
becomes
{TRUE; Simulated; False; False; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; Truthful}*{TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; Truthful; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; Truthful; TRUE; True}
Both conditions must be met, the asterisk lets us multiple the arrays significant AND logic.
True * True equals FALSE, all other combinations return Fake. TRUE * Faux equals FALSE and then on.
{Truthful; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; Fake; Truthful; True; True; Truthful} * {TRUE; True; TRUE; TRUE; Truthful; TRUE; Truthful; TRUE; Truthful; Truthful}
returns
{1; 0; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; one; 1; 1}.
Boolean values have numerical equivalents, True = one and Faux equals 0 (zippo). They are converted when y'all perform an arithmetics operation in a formula.
Step 4 - Create number sequence
The ROW function calculates the row number of a cell reference.
ROW(reference)
ROW($B$3:$East$12)
returns
{3; 4; 5; half-dozen; 7; viii; ix; 10; xi; 12}.
Step 5 - Create a number sequence from ane to n
The MATCH function returns the relative position of an item in an array or jail cell reference that matches a specified value in a specific order.
MATCH(ROW($B$3:$Due east$12), ROW($B$3:$E$12))
becomes
Lucifer({3; 4; 5; 6; 7; viii; 9; 10; 11; 12}, {iii; 4; 5; half dozen; 7; 8; 9; x; 11; 12})
and returns
{one; ii; 3; iv; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; x}.
Stride 4 - Return corresponding row number
The IF function returns one value if the logical test is TRUE and some other value if the logical test is Simulated.
IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
IF((Index($B$3:$Due east$12, , $D$16)< =$D$15)*(Alphabetize($B$3:$E$12, , $D$16)> =$D$14), Friction match(ROW($B$3:$E$12), ROW($B$3:$Due east$12)), "")
becomes
IF({i; 0; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 1; i; 1}, MATCH(ROW($B$iii:$E$12), ROW($B$three:$Eastward$12)), "")
becomes
IF({i; 0; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 1; 1; 1}, {1; ii; 3; iv; 5; 6; seven; eight; ix; ten}, "")
and returns
{ane; ""; ""; ""; 5; ""; seven; eight; 9; 10}.
Step 5 - Extract k-th smallest row number
The SMALL part returns the 1000-th smallest value from a group of numbers.
Pocket-sized(assortment,k)
SMALL(IF((INDEX($B$3:$Eastward$12, , $D$sixteen)< =$D$15)*(INDEX($B$iii:$E$12, , $D$16)> =$D$14), Lucifer(ROW($B$iii:$E$12), ROW($B$3:$East$12)), ""), ROWS(B20:$B$20))
becomes
Modest({1; ""; ""; ""; 5; ""; seven; 8; 9; 10}, ROWS(B20:$B$20))
becomes
Pocket-size({1; ""; ""; ""; 5; ""; 7; 8; 9; 10}, 1)
and returns 1.
Step six - Return the entire row record from prison cell range
The INDEX function returns a value from a cell range, you specify which value based on a row and column number.
INDEX(array,[row_num],[column_num])
INDEX($B$three:$E$12, Pocket-size(IF((Alphabetize($B$3:$E$12, , $D$16)< =$D$15)*(Index($B$3:$E$12, , $D$16)> =$D$14), Friction match(ROW($B$three:$East$12), ROW($B$3:$E$12)), ""), ROWS(B20:$B$20)), COLUMNS($A$1:A1))
becomes
INDEX($B$three:$Eastward$12, one, , ane)
and returns {2, "Ken Smith", 6, "North"}.
Recommended reading
Match two criteria and return multiple records
Excerpt records where all criteria match if non empty
Extract all rows that incorporate a value between this and that
Extract records betwixt two dates
Filter records based on a date range and a text string
Search for a text string in a data set up
Excerpt records containing negative values
Extract records containing digits [Formula]
Back to top
2. Extract all rows from a range based on range criteria - Excel 365

Update 17 December 2020,the new FILTER function is now available for Excel 365 users. Formula in prison cell B20:
=FILTER($B$three:$Eastward$12, (D3:D12<=D15)*(D3:D12>=D14))
Information technology is a regular formula, all the same, it returns an assortment of values and extends automatically to cells below and to the right. Microsoft calls this a dynamic array and spilled array.
The array formula below is for before Excel versions, it searches for values that encounter a range benchmark (cell D14 and D15), the formula lets you change the column to search in with cell D16.
This formula tin be used with whatever dataset size and shape. To search the first column, type 1 in cell D16.
Back to height
ii.1 Explaining array formula
Step 1 - Get-go condition
The less than character and the equal sign are both logical operators significant they are able to compare value to value, the output is a boolean value.
In this case,
D3:D12<=D15
Step 2 - Second condition
D3:D12>=D14
Step 3 - Multiply arrays - AND logic
(D3:D12<=D15)*(D3:D12>=D14)
Footstep 4 - Filter values
FILTER($B$3:$E$12, (D3:D12<=D15)*(D3:D12>=D14))
Dorsum to pinnacle
3. Extract all rows from a range that meet criteria in one column [Assortment formula]
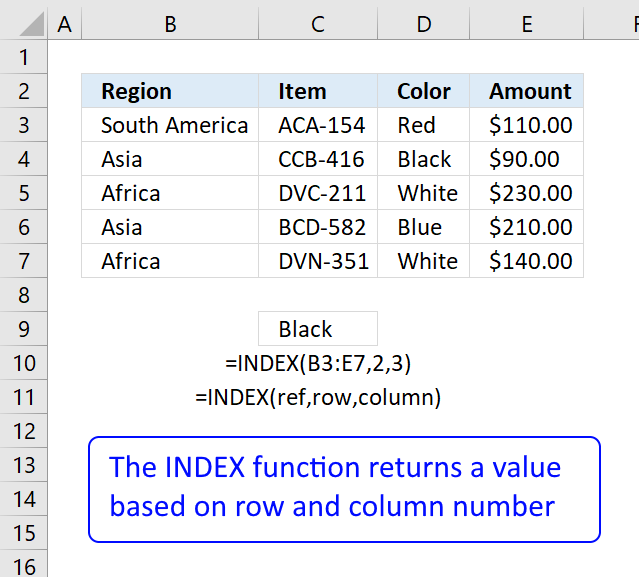
The array formula in prison cell B20 extracts records where cavalcade East equals either "Due south" or "East".
The following array formula in cell B20 is for earlier Excel versions than Excel 365:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$12, SMALL(IF(COUNTIF($E$15:$E$sixteen,$Due east$3:$Eastward$12), MATCH(ROW($B$3:$E$12), ROW($B$three:$E$12)), ""), ROWS(B20:$B$20)), COLUMNS($B$2:B2))
To enter an assortment formula, blazon the formula in a cell and so press and hold CTRL + SHIFT simultaneously, now press Enter once. Release all keys.
The formula bar now shows the formula with a beginning and ending curly bracket telling you that you entered the formula successfully. Don't enter the curly brackets yourself.
Back to pinnacle
3.i Explaining formula in prison cell B20
Pace i - Filter a specific column in jail cell range $A$ii:$D$xi
The COUNTIF function allows you to identify cells in range $E$3:$E$12 that equals $Due east$fifteen:$East$16.
COUNTIF($Eastward$15:$E$16,$E$3:$E$12)
becomes
COUNTIF({"South"; "East"},{"N"; "North"; "Southward"; "W"; "South"; "East"; "West"; "W"; "Southward"; "Due east"})
and returns
{0;0;ane;0;1;ane;0;0;i;one}.
Step 2 - Return corresponding row number
The IF part has three arguments, the first one must be a logical expression. If the expression evaluates to TRUE and then i matter happens (argument 2) and if Faux another thing happens (argument iii).
The logical expression was calculated in step 1 , Truthful equals 1 and FALSE equals 0 (zero).
IF(COUNTIF($E$15:$E$16,$East$3:$East$12), Lucifer(ROW($B$3:$Eastward$12), ROW($B$3:$Eastward$12)), "")
becomes
IF({0; 0; 1; 0; ane; ane; 0; 0; one; 1}, MATCH(ROW($B$3:$E$12), ROW($B$3:$Eastward$12)), "")
becomes
IF({0; 0; one; 0; 1; 1; 0; 0; i; 1}, {one; 2; 3; 4; 5; half dozen; 7; 8; ix; 10}, "")
and returns
{""; ""; 3; ""; 5; half dozen; ""; ""; ix; 10}.
Stride 3 - Find thou-th smallest row number
Small-scale(IF(COUNTIF($Eastward$fifteen:$E$16,$E$three:$E$12), Friction match(ROW($B$iii:$East$12), ROW($B$3:$Eastward$12)), ""), ROWS(B20:$B$20))
becomes
SMALL({""; ""; 3; ""; v; half dozen; ""; ""; ix; 10}, ROWS(B20:$B$20))
becomes
Small({""; ""; 3; ""; 5; 6; ""; ""; ix; ten}, one)
and returns three.
Step iv - Render value based on row and column number
The INDEX function returns a value based on a cell reference and column/row numbers.
Index($B$3:$Eastward$12, SMALL(IF(COUNTIF($Due east$15:$E$16,$East$3:$E$12), Lucifer(ROW($B$3:$E$12), ROW($B$3:$Due east$12)), ""), ROWS(B20:$B$20)), COLUMNS($B$2:B2))
becomes
INDEX($B$3:$E$12, iii, COLUMNS($B$2:B2))
becomes
INDEX($B$3:$Due east$12, 3, ane)
and returns 3 in cell B20.
Back to top
Recommended reading
- Match two criteria and return multiple records
- Extract records where all criteria match if not empty
- Excerpt all rows that contain a value between this and that
- Excerpt records between two dates
- Filter records based on a appointment range and a text string
- Search for a text string in a information set
- Extract records containing negative values
- Excerpt records containing digits [Formula]
Back to acme
4. Extract all rows from a range based on multiple conditions - Excel 365

Update 17 December 2020,the new FILTER function is now available for Excel 365 users. Formula in cell B20:
=FILTER($B$3:$E$12, COUNTIF(E15:E16, E3:E12))
Information technology is a regular formula, however, it returns an assortment of values. Read here how it works: Filter values based on criteria
The formula extends automatically to cells beneath and to the correct. Microsoft calls this a dynamic assortment and spilled array.
Back to top
4.i Explaining array formula
Step 1 -
COUNTIF(E15:E16, E3:E12)
Step 2 -
FILTER($B$3:$E$12, COUNTIF(E15:E16, E3:E12))
Back to top
5. Extract all rows from a range that meet criteria in one column [Excel divers Tabular array]
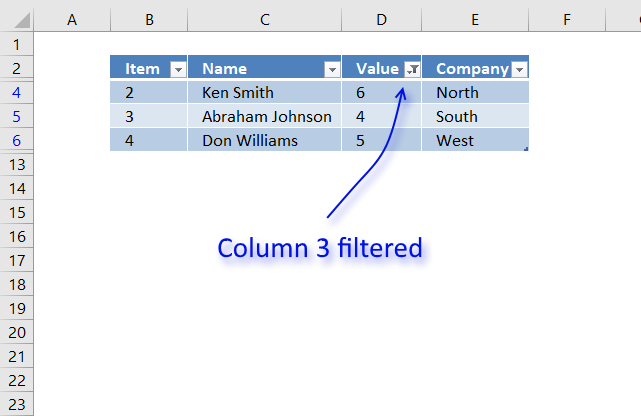
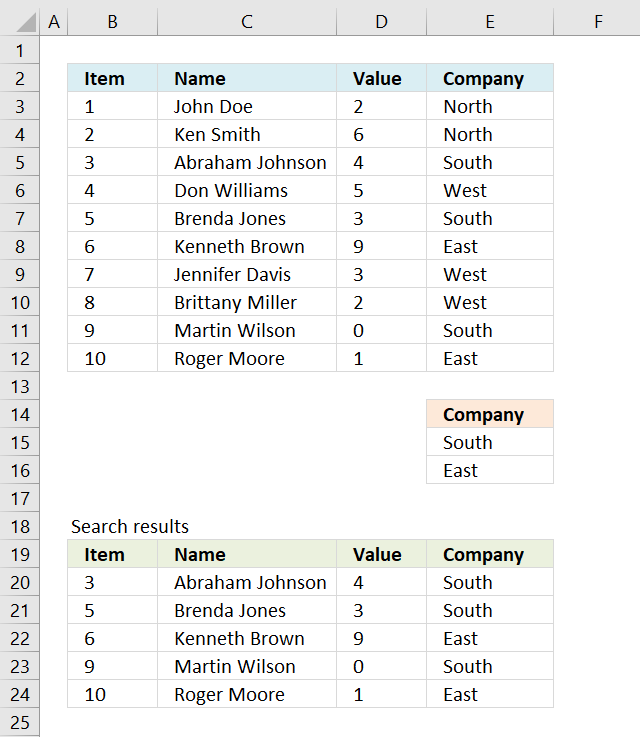
The image higher up shows a dataset converted to an Excel divers Table, a number filter has been applied to the tertiary cavalcade in the table.
Here are the instructions to create an Excel Table and filter values in column 3.
- Select a cell in the dataset.
- Press CTRL + T
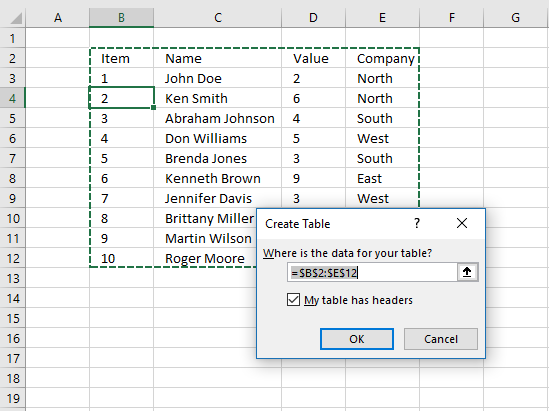
- Printing with left mouse push on check box "My tabular array has headers".
- Press with left mouse button on OK button.
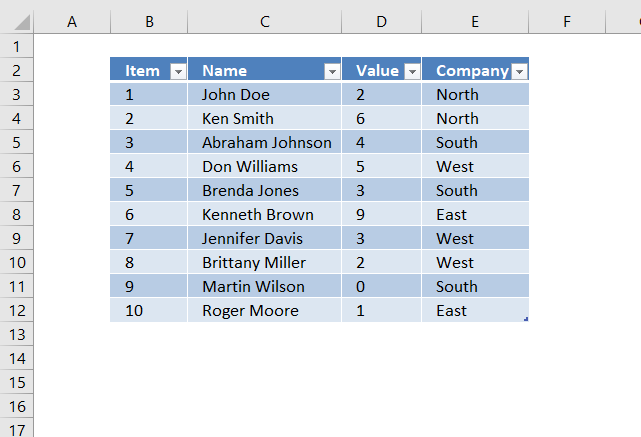
The paradigm above shows the Excel defined Tabular array, here is how to filter D between 4 and 6:
- Press with left mouse button on black arrow next to header.
- Printing with left mouse button on "Number Filters".
- Press with left mouse button on "Between...".
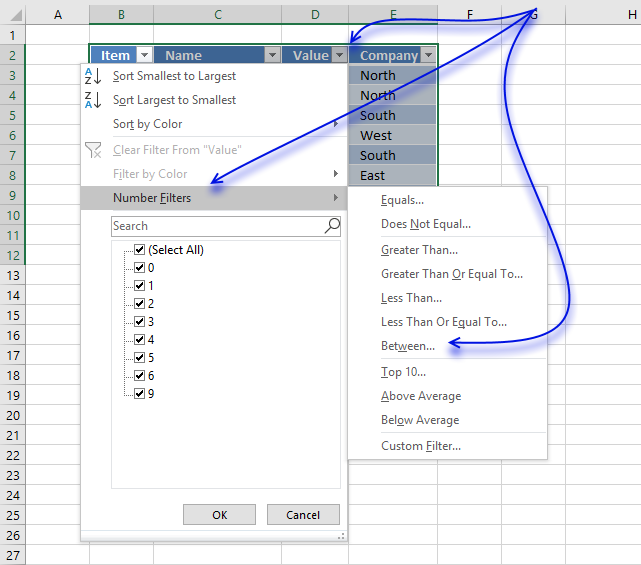
- Type iv and vi.
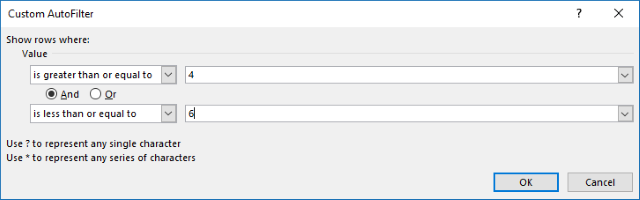
- Printing with left mouse button on OK push button.

Dorsum to top
half dozen. Extract all rows from a range that meet criteria in one column [Filter]
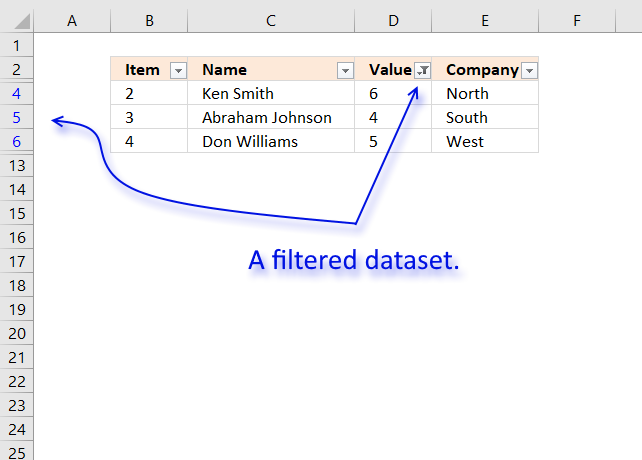
The image above shows filtered records based on two conditions, values in column D are larger or equal to 4 or smaller or equal to 6.
Here is how to use Filter arrows to a dataset.
- Select whatever cell within the dataset range.
- Become to tab "Data" on the ribbon.
- Printing with left mouse push button on "Filter push".
Black arrows appear next to each header.
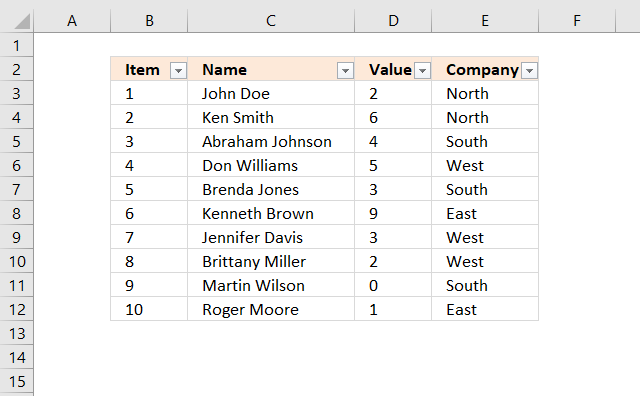
Lets filter records based on conditions applied to cavalcade D.
- Press with left mouse button on black arrow adjacent to header in Cavalcade D, see image below.
- Press with left mouse push on "Number Filters".
- Press with left mouse push button on "Between".
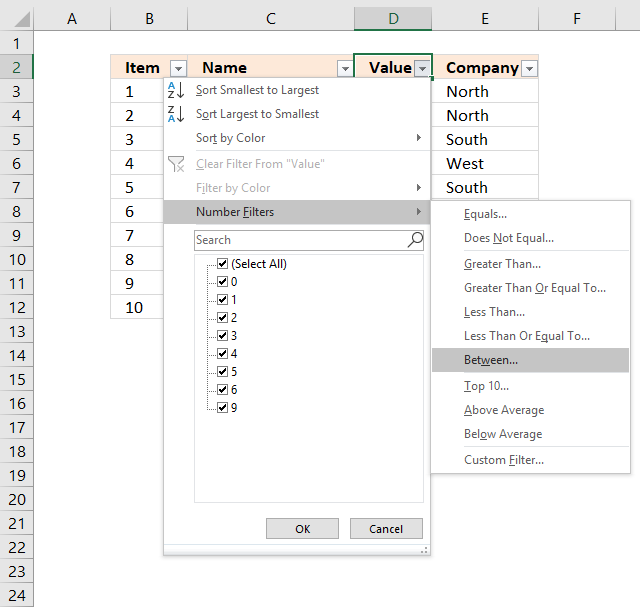
- Type 4 and 6 in the dialog box shown below.
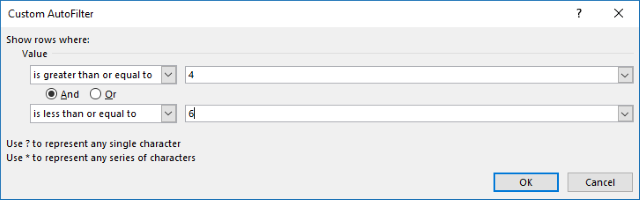
- Printing with left mouse push button on OK button.
Back to superlative
vii. Extract all rows from a range that encounter criteria in 1 cavalcade
[Advanced Filter]
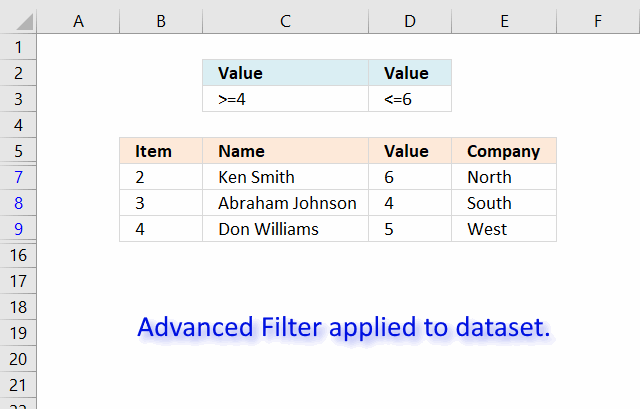
The image above shows a filtered dataset in cell range B5:E15 using Advanced Filter which is a powerful feature in Excel.
Here is how to apply a filter:
- Create headers for the column you want to filter, preferably higher up or beneath your data set.
Your filters will perchance disappear if placed next to the data set because rows may become subconscious when the filter is practical. - Select the entire dataset including headers.
- Go to tab "Information" on the ribbon.
- Printing with left mouse button on the "Advanced" button.
- A dialog box appears.
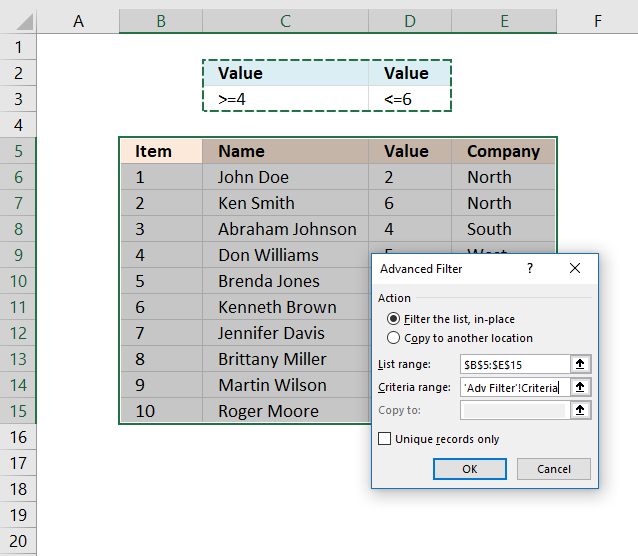
- Select the criteria range C2:D3, shown ithe due north in a higher place image.
- Press with left mouse push on OK push button.

Back to top
Recommended posts
Read this post and see how to extract duplicate records:
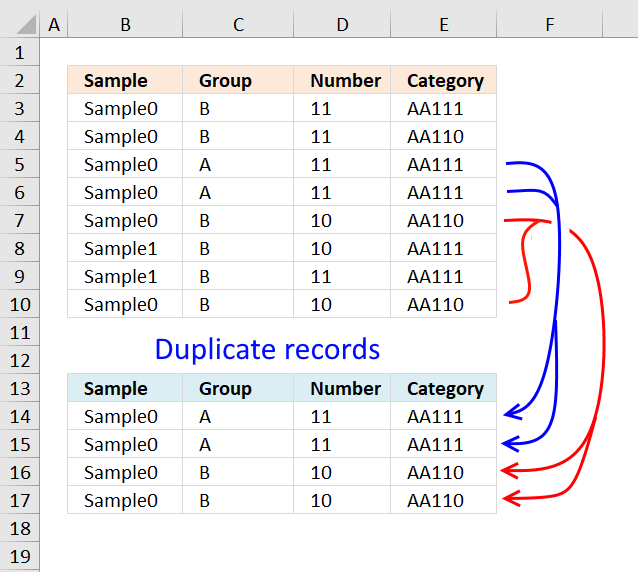
Excerpt duplicate records
This commodity describes how to filter duplicate rows with the use of a formula. It is, in fact, an assortment […]
Extract duplicate records
Learn how to filter unique distinct records:
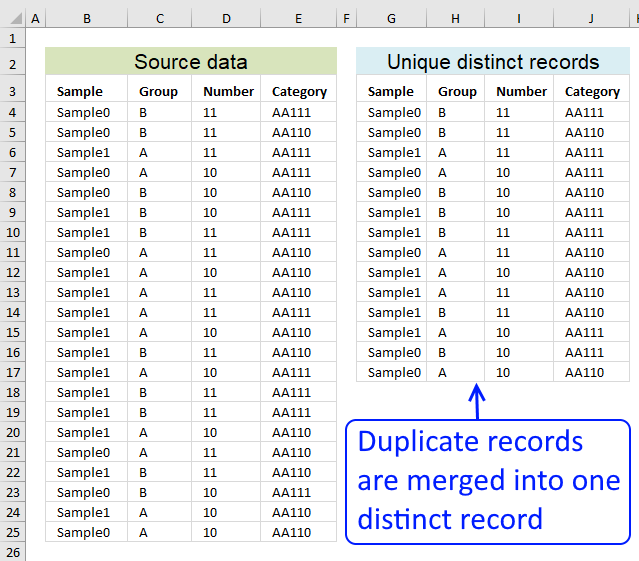
Filter unique distinct records
Table of contents Filter unique distinct row records Filter unique distinct row records but non blanks Filter unique distinct row […]
Filter unique distinct records
Back to top
8. Excel file
Source: https://www.get-digital-help.com/extract-all-rows-from-a-range-that-meet-criteria-in-one-column-in-excel/
0 Response to "How to Read Excel File Matlab Every 5th Row"
Post a Comment